The Importance Of Addressing Co-Occurring Disorders In Addiction
Addiction is a complex disease that often involves more than a physical dependence on a substance. Many people who struggle with addiction also suffer from co-occurring mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). These co-occurring disorders can exacerbate addiction and make recovery more challenging, so it is crucial to address them as part of the treatment process.
Understanding Co-Occurring Disorders
Co-occurring disorders, also known as dual diagnosis, refer to the presence of both a substance use disorder and a mental health disorder. According to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), approximately 9.2 million adults in the United States had both mental and substance use disorders in 2018.
Co-occurring disorders can be challenging to diagnose because the symptoms of one disorder can mask the symptoms of the other. For example, someone with depression may self-medicate with drugs or alcohol, which can lead to addiction. On the other hand, someone with an addiction may experience symptoms of anxiety or depression due to their substance use.

The Importance of Addressing Co-Occurring Disorders
Co-occurring disorders can complicate addiction treatment and make achieving and maintaining sobriety more difficult. For example, if someone with depression is not treated for their mental health disorder, they may be more likely to relapse into substance use. Addressing co-occurring disorders is crucial for achieving long-term recovery because it helps to address the root causes of addiction.
Integrated Treatment for Co-Occurring Disorders
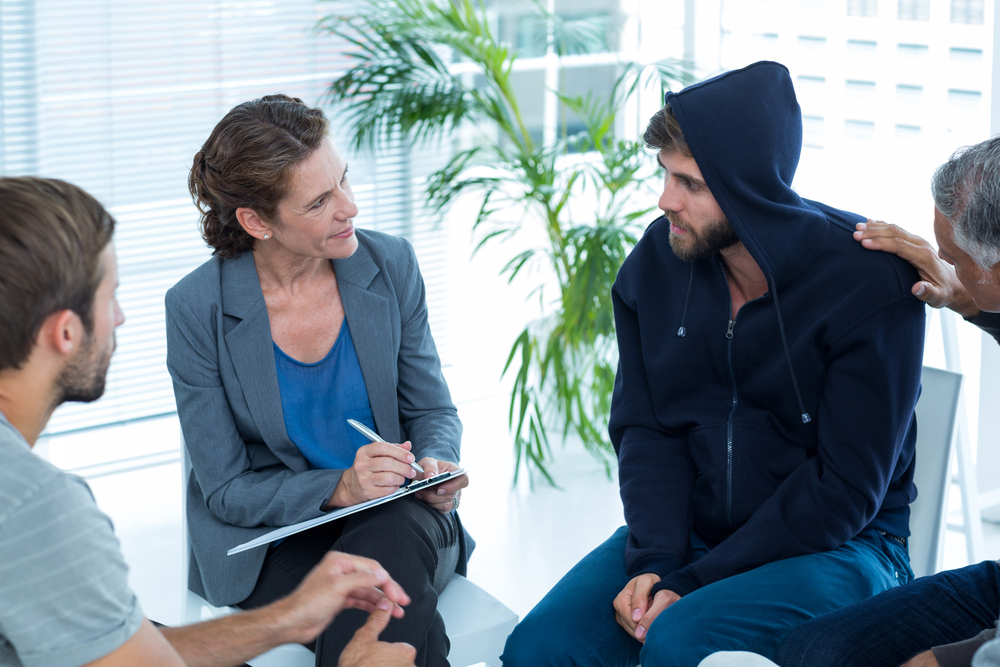
Integrated treatment is the most effective approach to address co-occurring disorders. Integrated treatment involves simultaneously addressing both the substance use disorder and the mental health disorder with the same treatment team. This approach helps to ensure that the treatment plan is comprehensive and addresses all aspects of the individual’s health and well-being.
Integrated treatment can involve a variety of evidence-based therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), and medication-assisted treatment (MAT). Integrated treatment aims to help individuals develop coping skills, manage their symptoms, and build a strong foundation for long-term recovery.

Signs and Symptoms of Co-Occurring Disorders
Co-occurring disorders can be challenging to diagnose, as the symptoms of one disorder can mask the symptoms of the other. However, there are some common signs and symptoms that may indicate the presence of a co-occurring disorder. These include:
- Increased substance misuse: Someone with a co-occurring mental health disorder may use drugs or alcohol to self-medicate, leading to increased substance use.
- Mood changes: Changes in mood, such as feeling sad or hopeless, can be a symptom of a mental health disorder and may also be present in addiction.
- Difficulty with daily activities: Someone with a co-occurring disorder may have difficulty performing daily activities such as work, attending school, or maintaining relationships.
- Social isolation: Individuals with co-occurring disorders may withdraw from social situations or isolate themselves from others.
- Physical symptoms: Physical symptoms, such as headaches or digestive issues, may be present in mental health disorders and addiction.
- Changes in behavior: Changes in behavior, such as increased aggression or impulsiveness, may also indicate the presence of a co-occurring disorder.
It’s important to remember that everyone’s experience with addiction and mental health disorders is different, and symptoms may vary from person to person. If you or someone you know is experiencing any of these symptoms, seek help from a qualified healthcare professional who can provide a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.

Contact Louisville Recovery Center
Addressing co-occurring disorders is crucial for effective addiction treatment and long-term recovery. Integrated treatment that addresses both substance use disorder and mental health disorder can help individuals develop the skills and tools they need to achieve and maintain sobriety. If you or a loved one is struggling with addiction and co-occurring mental health disorders, contact Louisville Recovery Center for help. Our team of experienced professionals can help you develop a personalized treatment plan that meets your unique needs and goals.